Dear students, if you are in Class 12 for the academic year 2024-25, this information is very important for you. Today, we are going to share a CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper through this website. This sample paper can be extremely useful for your exam, and with the help of these sample papers, you can score well in your examination.
Note: CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper has been created by experienced teachers, and some questions from it may appear in your exam.
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -9)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Economics (030)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
1. This question paper contains two sections :
Section A – Macro Economics
Section B – Indian Economic Development
2. This paper contains 20 Multiple Choice Type Questions of 1 mark each.
3. This paper contains 4 Short Answer Type Questions of 3 marks each to be answered in 60 to
80 words.
4. This paper contains 6 Short Answer Type Questions of 4 marks each to be answered in 80 to
100 words.
5. This paper contains 4 Long Answer Type Questions of 6 marks each to be answered in 100 to
150 words.
SECTION-A – Macro Economics
1. Read the following statements carefully:
Assertion (A): Revenue expenditure does not result in the creation of assets or reduction of liabilities.
Reason (R): Expenditures on salaries, pensions, and subsidies are examples of capital expenditure.
Choose the correct option from those given below:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
2. “The country has adopted a managed floating exchange rate system, wherein the currency’s exchange rate is primarily determined by market forces but with occasional interventions by the central bank to stabilize excessive volatility.”
Source: [RBI Annual Report, 2023](https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/AnnualReportPublications.aspx?year=2023)
Which of the following best describes a managed floating exchange rate system?
(A) Exchange rate fixed by the government
(B) Exchange rate determined purely by market forces
(C) Exchange rate pegged to a basket of currencies
(D) Exchange rate determined by market with central bank interventions
3. Depreciation, which represents the wear and tear of capital goods over time, is also commonly referred to as ________ consumption of fixed capital in national income calculations.
Choose the correct option to fill in the blank.
(A) Gross
(B) Net
(C) Normal
(D) Abnormal
4. When the central bank reduces the ________ Ratio, commercial banks have more funds available to extend as loans, thereby increasing the money supply.
Choose the correct option to fill in the blank.
(A) Cash Reserve
(B) Bank
(C) Reverse Repo
(D) Marginal Standing Facility
5. From the given diagrams, identify the correct option that indicates the ‘Investment Line’ passing through the origin drawn at a particular angle.
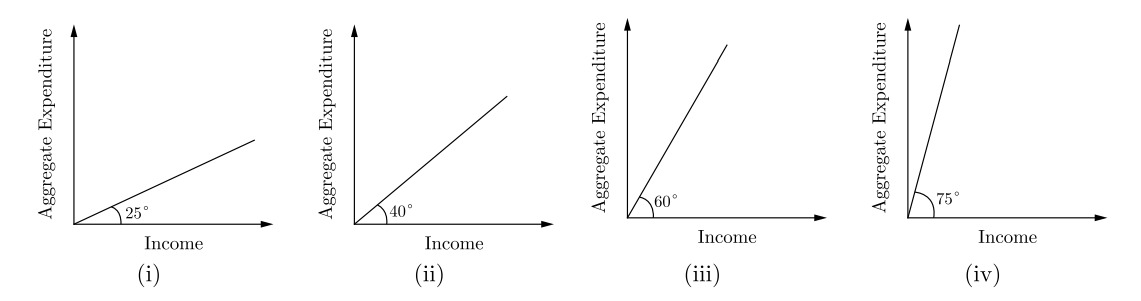
(A) (iv)
(B) (ii)
(C) (iii)
(D) (i)
6. Expenditures that do not result in the creation of assets or reduction of liabilities are known as ______ expenditure.
Choose the correct option to fill in the blank.
(A) Capital
(B) Revenue
(C) Development
(D) Non-Plan
7. Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Under a fixed exchange rate system, the value of a currency is set by the government or monetary authority and does not fluctuate with changes in the foreign exchange market.
Statement 2: A flexible exchange rate system allows the currency value to be determined by supply and demand forces in the foreign exchange market without any government intervention.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct option from the following:
(A) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
(B) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
8. When computing the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at market prices, we consider the monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. To obtain the Net Domestic Product (NDP) at market prices, we need to subtract _______ from the GDP to account for the wear and tear of capital goods.
Choose the correct option to fill in the blank.
(A) Indirect Taxes
(B) Depreciation
(C) Net Factor Income from Abroad
(D) Subsidies
9. Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: An increase in the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by the central bank reduces the lending capacity of commercial banks, thereby decreasing the money supply in the economy to control inflation.
Statement 2: A decrease in the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requires banks to hold more liquid assets, such as cash and government securities, thus reducing their ability to create credit.
In light of the given statements, Choose the correct option from the following:
(A) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
(B) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(C) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
10. According to the diagram, exports in services during April-January 2023-24 are __________ by USD _____ billion compared to April-January 2022-23.
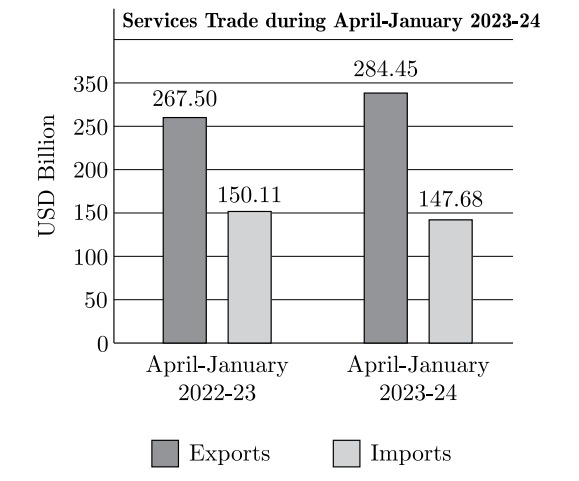
(Choose the correct option to fill up the blank)
(A) higher, 16.95
(B) higher, 15.35
(C) lower, 16.95
(D) lower, 15.35
11. Calculate ‘Gross National Product at Factor Cost’ (GNP,c) from the following data by expenditure method.

12. Describe any three sources of demand for foreign exchange.
OR
What is Balance of Payments? Give meanings of trade balance and current account balance.
13. Derive the formula, K = 1/MPS
Where K = Investment Multiplier
MPS = Marginal Propensity to Save
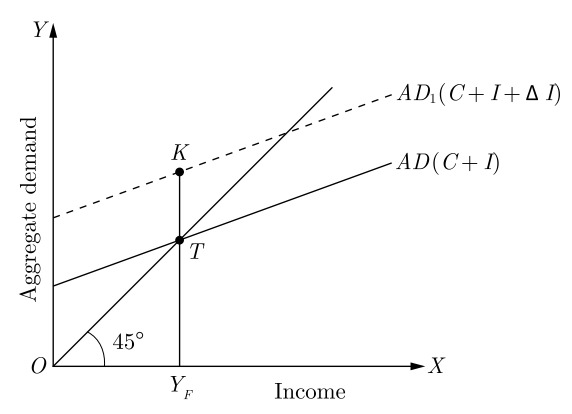
14. In the given figure, what does the gap ‘KT’ represent ? State and discuss any two fiscal measures to correct the situation.
15. Read the given excerpt taken from the article ‘What is ‘Money” published by The Economic Times on 20th September 2022
“The money came into existence to overcome the drawbacks of the barter system. Earlier, people used to exchange goods and services as a form of commerce. This often led to many disadvantages, one of which was the double coincidence of wants. To solve this problem, a standard medium of exchange, money, was introduced.”
Explain in brief the function of money highlighted in the given excerpt.
OR
Define credit multiplier. What role does it play in determining the credit creation power of the banking system? Use a numerical illustration to explain.
16. (i) “Management of a water polluting oil refinery says that the it (oil refinery) ensures welfare through its contribution to Gross Domestic Product”. Defend or refute the argument of management with respect to GDP as a welfare measure of the economy.
(ii) Giving reason, explain the treatment assigned to the following while estimating national income
(a) Interest paid by banks on deposits by individuals
(b) National debt interest
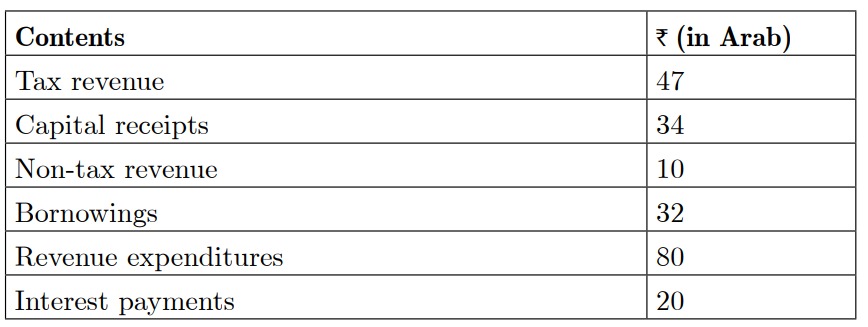
17. (i) From the following data about a government budget, find out the following:
(a) Revenue deficit
(b) Fiscal deficit
(c) Primary deficit
(ii) Explain the budgetary measures for achieving the objective of setting up of production units in backward regions.
OR
(i) Classify the following taxes into direct and indirect tax. Give reasons for your answer.
(a) Corporation tax
(b) Entertainment tax
(c) Excise duty
(ii) Distinguish between primary and revenue deficit?
S-B – Indian Economic Development
18. What does picture indicate about the movement of labour?

(A) Informalisation of workforce
(B) Casualisation of workforce
(C) Jobless growth
(D) Either (A) or (B)
19. Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Small Scale Industries (SSIs) were considered unimportant in India’s economic framework post-independence.
Statement 2: The Industrial Policy Resolution of 1956 aimed to regulate and control key industries through state ownership.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct option from the following:
(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
20. Read the following statements carefully: Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose the correct option from those given below:
Assertion (A): Privatization under the LPG policy resulted in complete government withdrawal from all public sector enterprises.
Reason (R): Privatization aimed to enhance efficiency by involving the private sector in formerly state-owned enterprises.
Options:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
21. The expansion of the education sector in India has significantly contributed to the enhancement of ______ and ______, which are critical components of human capital.
Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.
(A) agricultural productivity; industrial output
(B) technological innovation; military strength
(C) infrastructure development; foreign trade
(D) human capital; economic development
22. Agricultural diversification in rural India includes which of the following?
Which of the following is/are correct ?
(i) Shifting to cash crops
(ii) Engaging in allied activities
(iii) Adopting organic farming
(iv) Increasing livestock production
Option :
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(C) (i), (iii), and (iv)
(D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
23. Which of the following are effects of economic development on the environment?
Which of the following is correct ?
(A) Increased biodiversity
(B) Improved air quality
(C) Enhanced natural resource conservation
(D) Deforestation and pollution
24. Which of the following factors have contributed to China’s rapid economic growth compared to India?
Which of the following is correct ?
(A) Lower investment in infrastructure
(B) Less emphasis on education
(C) Strong government planning and export-oriented policies
(D) Restricted foreign investment
25. Which of the following statements correctly describes the occupational structure of India on the eve of independence?
Which of the following is correct ?
(A) Majority of the population was employed in the industrial sector
(B) Services sector was the largest employer
(C) Agriculture employed the majority of the population
(D) High percentage of workforce in the IT sector
26. “During the Green Revolution in the 1960s and 1970s, India introduced high-yielding variety seeds, modern irrigation facilities, and chemical fertilizers to boost agricultural production.
While this strategy led to a significant increase in food grain output, it also resulted in regional disparities and benefited mainly the wealthy farmers.”
Which of the following was a major drawback of the new agricultural strategy?
(A) Decrease in overall agricultural production
(B) Equitable distribution of benefits among all farmers
(C) Neglect of small and marginal farmers leading to increased inequalities
(D) Reduction in the use of modern technology in agriculture
27. Which of the following is a feature of globalization as per the LPG policy?
Which of the following is correct ?
(A) Isolation of the Indian economy from global markets
(B) Increased foreign investment and trade
(C) Restriction on technology transfer
(D) Emphasis on self-reliance and closed markets
28. The figure given below depicts that India’s environmental problems pose a dichotomy- they are poverty induced and at the same time arise due to affluence in living standards. Do you agree with the given statement? Justify.

29. Bring out the need for on-the-job-training for a person.
OR
Defend or refute the statement with valid explanation.
“There are more number of regular salaried employees found in urban areas than in rural areas”.
30. India and China show contrasting demographic trends as per the World Development Indicators, 2015. India’s annual population growth rate was 1.2%, significantly higher than China’s 0.5%, reflecting faster expansion. The gender ratio in India stood at 929 females per thousand males, while China reported a slightly better ratio of 941. These variations highlight the impact of differing policies and socio-economic factors on their populations. Source World Development Indicators, 2015
31. (i) Give the meaning of demonetisation?
(ii) Discuss briefly any two major steps taken by the Government of India on ‘Financial Sector’ front under the Economic Reforms of 1991.
OR
Deepesh argues that in the era of privatisation, there is no need for government intervention in education and health sectors. However, his friend Mahesh argues that education and health care services create social benefits and therefore there is a need for government intervention in education and health sectors. Decide with reasons, who is right?
32. State whether the following statements are true or false, with valid arguments.
(i) Substituting fertiliser subsidies with agricultural subsidies as the farmer was benefitting fertiliser industry and not the target group has been the topic of immense debate regarding provision of subsidies during 1960’s and 70’s.
(ii) The main reason for constituting Karve Committee in 1955 was setting capital good industries in rural areas and thus promoting rural development.
33. Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding.
One of the most compelling reasons for studying environmental science and management is the fact that, in the view of many leading authorities, we are now experiencing an environmental crisis, indeed, many authors have claimed that the present environmental crisis is unprecedented in its magnitude, pace and severity (Park 2001). Awareness of this environmental crisis has grown since the 1970s, partly as a result of the prominence given to major so-called ‘environmental’ disasters such as the Sahelian droughts of the 1970s and 1980s and the nuclear accident at Chernobyl in 1986.
A major assessment of the global environment published in 1999, the UNEP Global Environment
Outlook 2000 Report (UNEP 1999), drew attention to two critical, recurring themes
- the fact that the global human ecosystem is threatened by grave imbalances in productivity and in the distribution of goods and services as evidenced by the fact that a large proportion of the human population lives in poverty and that a widening gap exists between those who benefit from economic and technological development and those who do not.
- the fact that accelerating changes are occurring at the global scale, with rates of economic and social development outstripping progress in achieving internationally co-ordinated environmental stewardship-with the result that improvements in environmental protection due to new technologies are being ‘cancelled out’ by the magnitude and pace of human population growth and economic development.
Consequently, a wide range of environmental problems has emerged, those problems include anthropogenic climate change (‘global warming’), the depletion of stratospheric ozone (the ‘ozone hole’), the acidification of surface waters (‘acid rain’), the destruction of tropical forests, the depletion and extinction of species, and the precipitous decline of biodiversity. Yet, while all of these problems have physical (environmental) manifestations, their causes – and their potential solutions – are invariably bound up with human attitudes, beliefs, values, needs, desires, expectations and behaviours. Thus, the symptoms of the environmental crisis cannot be regarded purely as physical problems requiring solutions by environmental ‘specialists’, instead, they are intrinsically human problems and they are intimately related to the question of what it means to be human.
(i) “Opportunity costs of negative environ-mental impact are high.” Comment.
(ii) There exists a positive correlation between environmental sustainability and economics
development. Do you agree? Give suitable reason in support of your answer.
34. (i) Define worker population ratio.
(ii) What do you understand by the term ‘distress sale’?
(iii) Literacy rates in India have increased but so has the absolute number of illiterates. Why?
OR
(i) Enlist some problems faced by farmers during the initial years of organic farming.
(ii) “In recent times, the Indian economy has experienced the problem of casualisation of the workforce. This problem has only been aggravated by the outbreak of Covid-19.”
Do you agree with the given statement? Discuss any two disadvantages of casualisation of the workforce in the light of the above statement.
Check Also:
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -4)
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -7)
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -8)
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -3)
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -2)
-
CBSE Board Class 12 Economics Sample Paper (Set -1)