If you are a CBSE Class 12 student and Political Science is one of your subjects, then CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1) is extremely important for you. Through this post, we are providing you with free CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Papers to help you prepare effectively for your board exams.
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
These high-quality sample papers are designed to give you a clear understanding of the exam pattern and improve your performance. We hope that practicing these papers will enhance your preparation and enable you to score excellent marks in your board exams. Make the most of this opportunity and give your preparation the edge it needs!
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Political Science (028)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
3. Section A questions number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries. 1 mark.
4. Section B questions number 13 to 18 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
2 marks. Write answer to each question in 50 to 60 words.
5. Section C questions number 19 to 23 are Long Answer Type-I question. Each question carries
4 marks. Write answer to each question in 100 to 120 words.
6. Section D questions number 24 to 26 are Passage, Cartoon and Map-based questions.
Answer each question accordingly.
7. Section E questions number 27 to 30 are Long Answer Type-II questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
Write answer to each question in 170 to 180 words.
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, note that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
Section-A
1. The Soviet Union’s political structure was characterized by a single-party system.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about the Soviet System?
(A) The Communist Party was the only legal political party in the Soviet Union.
(B) The Soviet economy was based on centralized planning and state ownership.
(C) Multiple political parties competed in free and fair elections.
(D) The government controlled all aspects of media and public discourse.
2. In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason(R).
Choose the appropriate answer from the options given below as the correct answer:
Assertion (A): The European Union facilitates the free movement of goods, services, and people
among its member states.
Reason (R): The Euro is the official currency of all European Union member countries.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
3. Match the terms given in column ‘A’ correctly with their meaning given in column ‘B’ and choose the appropriate code as the correct answer:
Column A
1. Military in Pakistan
2. Democracy in Bangladesh
3. Monarchy in Nepal
4. Ethnic Conflict in Sri Lanka
Column B
(i) The role of the military has often disrupted democratic processes in this country.
(ii) Struggles and transitions towards stable democratic governance after periods of political unrest.
(iii) A form of government that was replaced by a federal democratic republic in 2008.
(iv) Long-standing tensions between different ethnic groups impacting national unity.
Codes:
(A) 1-(i), 2-(ii), 3-(iii), 4-(iv)
(B) 1-(ii), 2-(i), 3-(iv), 4-(iii)
(C) 1-(iii), 2-(iv), 3-(i), 4-(ii)
(D) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(ii), 4-(i)
4. Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The United Nations is the only international organization responsible for maintaining international peace and security.
Statement II: Other international organizations like NATO also contribute to maintaining peace and security.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(C) Statement I is true, but Statement II is false
(D) Statement I is false, but Statement II is true
5. Arrange the following security concepts in the order they were introduced:
I. Traditional Security
II. Human Security
III. Cooperative Security
IV. Comprehensive Security
Choose the correct option:
(A) I, II, III, IV
(B) I, III, II, IV
(C) II, I, III, IV
(D) I, II, IV, III
6. Identify and write the Incorrect pair:
(A) Montreal Protocol – Agreement to protect the ozone layer
(B) Kyoto Protocol – Agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
(C) Paris Climate Agreement – Agreement to combat climate change
(D) Stockholm Convention – Agreement to promote fossil fuels
7. Which significant event symbolized the official beginning of India’s journey toward gaining complete independence from British colonial rule?
(A) The Salt March initiated by Mahatma Gandhi to protest the British salt tax
(B) The Partition of Bengal, which divided the province into two separate parts
(C) The Partition of India, which led to the creation of two sovereign states, India and Pakistan
(D) The Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, where British forces fired on a peaceful gathering
8. The Congress Party’s dominance in the early decades of Indian democracy was largely attributed to ____________.
(A) The support of industrialists and rural leaders
(B) Its role in the national freedom struggle
(C) Foreign influence and investment
(D) Policies focused solely on urban development
9. The Second Five Year Plan, influenced by P.C. Mahalanobis, aimed for ____________.
(A) Boosting agricultural productivity through modern methods
(B) Rapid industrialization with emphasis on heavy industries
(C) Increased trade liberalization and foreign investment
(D) Extensive focus on healthcare and education sectors
10. Who was the prominent Indian leader that held the dual role of Prime Minister and Foreign Minister, shaping India’s early foreign policy?
(A) Lal Bahadur Shastri
(B) Sardar Patel
(C) Jawaharlal Nehru
(D) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
11. The term “Aya Ram, Gaya Ram” emerged in Indian politics to describe ____________.
(A) Frequent political defections by elected representatives
(B) The swift change in public opinion
(C) Rapid economic fluctuations
(D) Leaders changing their political ideologies
12. Which party joined the Janata Party alliance after splitting from Congress, led by Jagjivan Ram?
(A) Congress (Indira)
(B) Congress for Democracy
(C) Socialist Party
(D) Bharatiya Kranti Dal
Section-B
13. Name any two important specialized agencies of the United Nations that work in various fields globally.
14. What are the two Directive Principles of State Policy relating to foreign affairs policy?
15. What were the significant factors and underlying reasons that contributed to the dominance of the Congress Party in Indian politics until the year 1967?
16. What do you mean by the non-traditional notion of security?
17. Highlight any two features of Soviet System.
18. What were the impacts of the elections of 1989 on Indian politics?
Section-C
19. Mention the objectives of Nehru’s Foreign Policy. What was the strategy through which he wanted to achieve them?
20. ‘Democracy is becoming the first choice of the people of South Asia’. Justify the statement.
21. What are the two kinds of movement that were going on in North-East India?
22. Why do some economists describe economic globalisation as recolonization of the world?
23. “States have common but differentiated responsibilities towards environment”. Substantiate statement giving suitable examples.
Section-D
24. Study the given cartoon and answer the questions that follow.

(i) Which two leaders were among those who won the 1977 elections?
(A) Morarji Desai and Atal Bihari Vajpayee
(B) Charan Singh and Raj Narain
(C) Jagjivan Ram and Charan Singh
(D) All of the above
(ii) What does MISA stand for?
(A) Maintenance of Internal Security Act
(B) Management of Internal Security Act
(C) Monitoring of Internal Security Act
(D) Maintenance of International Security Act
(iii) Why was the Congress voted out of power in 1977?
(A) Imposition of emergency
(B) 42nd Amendment of the Constitution
(C) Censorship of the press
(D) All of the above
(iv) What was a significant misuse of power during the emergency period?
(A) Misuse of preventive detention laws
(B) Introduction of the Right to Information Act
(C) Implementation of the Green Revolution
(D) Expansion of welfare schemes
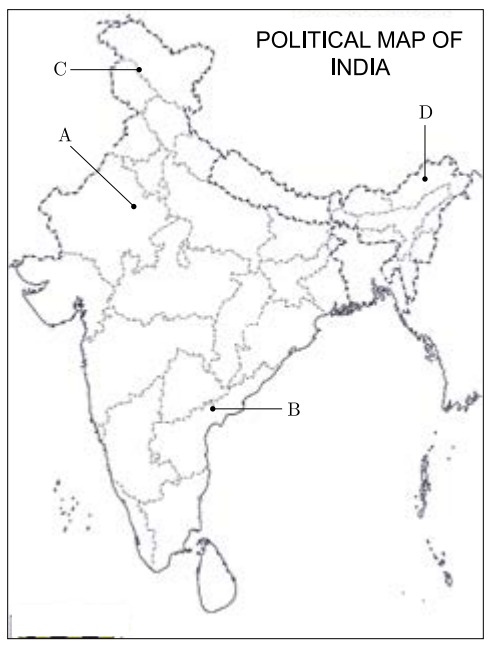
25. Study the political outline map of the India given below in which five different states have been marked as A, B, C and D. Identify correct states and name them. Consider about the Assembly Election results of 1967.
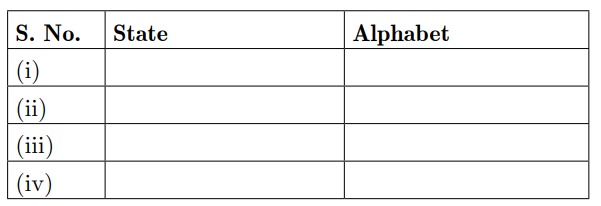
(i) The state where Congress did not get majority but formed government with the help of others.
(ii) The Mountaneous state where Congress got majority.
(iii) The Southern states where Congress got majority.
(iv) The North-Eastern states where Congress did not get the majority.
26. Study the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Nepal’s transition to democracy is not complete. At the moment, Nepal is undergoing a unique moment in its history because it is moving towards the formation of a Constituent Assembly that will write the Constitution for Nepal. Some sections in Nepal still think that a nominal monarchy is necessary for Nepal to retain its link with the past. The Maoist groups have agreed to suspend armed struggle. They want the Constitution to include the radical programmes of social and economic restructuring. All the parties in the SPA may not agree with this programme. The Maoists and some other political groups are also deeply suspicious of the Indian Government and its role in the future of Nepal.
(i) How is Nepal is undergoing a unique movement in its history?
(A) As it is moving towards the formation of Constituent Assembly that will write the constitution.
(B) As it is moving towards uncivilised protests and movement.
(C) Due to nominal monarchy in Nepal.
(D) None of the above
(ii) Why were some political parties suspicious in Nepal?
(A) Because they were deeply suspicious regarding the role of Indian Government in the future of Nepal.
(B) Because they were against the democratic set-up.
(C) Because they were suspicious regarding the social restructuring.
(D) All of the above
(iii) In the above passage, SPA stands for_____.
(A) State Party Alliance
(B) Seven Party Alliance
(C) Six Party Alliance
(D) Static Party Alliance
(iv) In which year the king of Nepal dismissed government and abolished the parliament?
Section-E
7. What were the effects of Emergency on the following aspects for our polity.
(i) Effects on civil liberties for citizens.
(ii) Impact on relationship between the Executive and Judiciary.
(iii) Functioning of Mass Media.
(iv) Working of Police and Bureaucracy.
OR
Explain the idea of Socialism advocated by Ram Manohar Lohia.
28. What do you mean by global poverty? What are the ways which can help in reducing disparity between the poor and the rich at the global level?
OR
Distinguish between the internal and external notion of traditional security.
29. Give examples to show that most of former Soviet republics were prone to conflicts and tensions.
OR
What was the Soviet System? Assess any four features of the Soviet system.
30. Define the process of Nation-Building. Discuss Nehru’s approach towards Nation-Building.
OR
“The accommodation of regional demands and the formation of linguistic states were also seen as more democratic”. Justify the statement with any three suitable arguments.
Read Also:
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 1
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 2
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 3
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 4
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 5
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 6
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 7
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 8