If you are a CBSE Class 12 student and Political Science is one of your subjects, then CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1) is extremely important for you. Through this post, we are providing you with free CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Papers to help you prepare effectively for your board exams.
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
These high-quality sample papers are designed to give you a clear understanding of the exam pattern and improve your performance. We hope that practicing these papers will enhance your preparation and enable you to score excellent marks in your board exams. Make the most of this opportunity and give your preparation the edge it needs!
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -7)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Political Science (028)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
3. Section A questions number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries. 1 mark.
4. Section B questions number 13 to 18 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
2 marks. Write answer to each question in 50 to 60 words.
5. Section C questions number 19 to 23 are Long Answer Type-I question. Each question carries
4 marks. Write answer to each question in 100 to 120 words.
6. Section D questions number 24 to 26 are Passage, Cartoon and Map-based questions.
Answer each question accordingly.
7. Section E questions number 27 to 30 are Long Answer Type-II questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
Write answer to each question in 170 to 180 words.
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, note that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
Section-A
1. Globalisation refers to the increasing interconnectedness of the world. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about the Concept of Globalisation?
(A) Globalisation involves the integration of economies, cultures, and political systems.
(B) Advances in technology have significantly facilitated the process of globalisation.
(C) Globalisation has led to the isolation of national economies from each other.
(D) The movement of goods, services, and people across borders is a key feature of globalisation.
2. Assertion (A): The Soviet Union was a single-party state controlled by the Communist Party.
Reason (R): The Communist Party allowed multiple parties to compete for power within the Soviet political system.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
3. Match the terms given in column ‘A’ correctly with their meaning given in column ‘B’ and choose the appropriate code as the correct answer:
Column A
1. European Union
2. ASEAN
3. Belt and Road Initiative
4. Rise of China
Column B
(i) A regional organization promoting economic and political cooperation in Southeast Asia.
(ii) A comprehensive infrastructure and economic project initiated by China to enhance global trade connectivity.
(iii) A political and economic union of 27 European countries facilitating free movement and a common market.
(iv) The increasing economic and geopolitical influence of China on the global stage.
Codes:
(A) 1-(iii), 2-(i), 3-(ii), 4-(iv)
(B) 1-(i), 2-(iii), 3-(iv), 4-(ii)
(C) 1-(ii), 2-(iv), 3-(i), 4-(iii)
(D) 1-(iv), 2-(ii), 3-(iii), 4-(i)
4. Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Military coups in Pakistan have disrupted the establishment of stable democratic governance.
Statement II: The military in Pakistan has always supported democratic institutions without interference.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(C) Statement I is true, but Statement II is false
(D) Statement I is false, but Statement II is true
5. Arrange the following United Nations principal organs in the order of their establishment:
I. General Assembly
II. Security Council
III. International Court of Justice
IV. Economic and Social Council
Choose the correct option:
(A) I, II, III, IV
(B) I, II, IV, III
(C) II, I, III, IV
(D) I, IV, II, III
6. Identify and write the Incorrect pair:
(A) Traditional Security – Focuses on military threats
(B) Non-Traditional Security – Includes issues like terrorism and environmental threats
(C) Human Security – Only pertains to economic stability
(D) Cooperative Security – Emphasizes collaboration among nations to ensure mutual safety
7. The Dravidian movement initially aimed for a separate Dravida Nadu but ultimately focused on regional pride and achieved political power through ____________.
(A) Armed struggle
(B) Electoral platform and democratic means
(C) National-level alliances
(D) Economic policies
8. The implementation of the Mandal Commission’s recommendations in 1990 led to ____________.
(A) Reservations for Scheduled Tribes only
(B) Large-scale protests over OBC reservations
(C) Support from all political groups
(D) An immediate decline in caste-based politics
9. Which of the following princely states initially expressed a desire to remain independent rather than joining either India or Pakistan after independence?
(A) The princely state of Junagadh, located in present-day Gujarat
(B) The northeastern state of Manipur, with its unique cultural identity
(C) Hyderabad, a wealthy state ruled by a Nizam who sought independence
(D) The disputed region of Kashmir, known for its scenic beauty and strategic importance
10. In which year did the Communist Party of India form the first democratically elected Communist government in the state of Kerala?
(A) 1947
(B) 1952
(C) 1957
(D) 1962
11. During the early years after independence, India’s development model was often viewed as a balance between ____________.
(A) Western capitalism and Soviet communism
(B) Import substitution and export orientation
(C) Nationalization and liberalization
(D) Capitalism and socialism
12. What was one key reason for the strain in Indo-China relations during the 1950s and 1960s?
(A) China’s support for India’s nuclear program
(B) India’s asylum to the Dalai Lama and Tibetan refugees
(C) India’s alliance with NATO
(D) China’s advocacy for India’s independence
Section-B
13. Highlight any two threats to a country’s security as per the traditional notion of security.
14. What does defection stand for in Indian politics? Highlight any two demerits of this practice.
15. Why did the Soviet Union disintegrate? Highlight any two arguments in support of your answer.
16. How the era of multi-party system led to the era of coalition at the centre?
17. Why were the states reorganised on linguistic basis in India in 1956?
18. Does globalisation leads to cultural homogenisation or cultural heterogenization or both? Justify.
Section-C
9. Highlight any two sources of threats being faced by the third world countries.
20. How the movement for secession in the Mizo Hills area gained popular support? How was this problem resolved?
21. Elaborate the change in the electoral performance of the Congress party and BJP, from the year 1984 to 2004.
22. What is globalisation? What is the difference between globalisation and internationalisations?
23. What are the four reasons behind the formation of ASEAN?
Section-D
24. Study the given cartoon and answer the questions that follow.

(i) Who is the person holding the placard that says ‘Save Democracy’?
(A) Indira Gandhi
(B) Jayaprakash Narayan
(C) Morarji Desai
(D) Charan Singh
(ii) To which political party does the group of five persons belong?
(A) Congress Party
(B) Janata Party
(C) Bharatiya Jana Sangh
(D) Communist Party
(iii) What is the intention of the person sitting on ‘Dharna,’ according to the group of five?
(A) To grab power and create chaos
(B) To oppose democracy
(C) To promote economic reforms
(D) To support monarchy
(iv) What does the placard ‘Save Democracy’ signify in this context?
(A) Support for monarchy
(B) Protest against authoritarianism
(C) Call for economic reforms
(D) Promotion of a single-party system
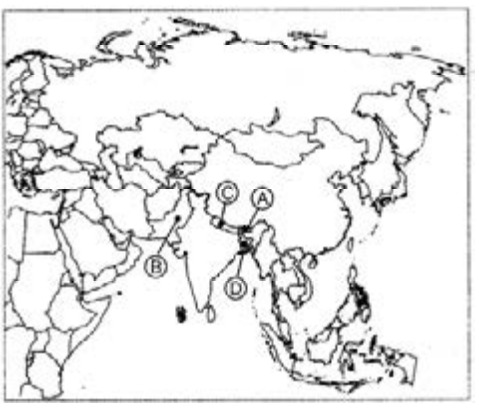
25. In the given outline map of South Asia, five countries have been marked as A, B, C and D. Identify them on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book with their respective serial number of the information used and the alphabet concerned as per the following format.
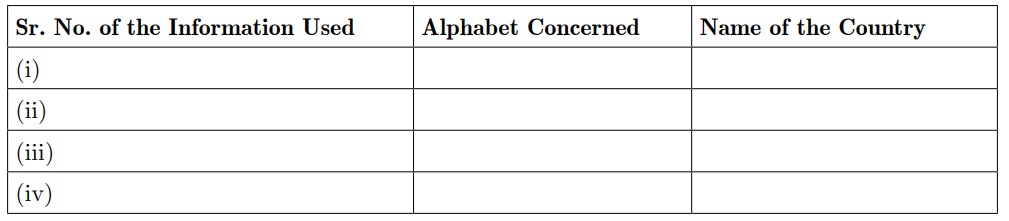
(i) The country has experienced both civilian as well as military rule.
(ii) Democracy was restored in this country in 2006.
(iii) This country is still a monarchy.
(iv) This country is a part of India’s ‘Look East Policy via Myanmar’.
26. Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.
What does independence consist of? It consists fundamentally and basically of foreign relations. That is the test of independence. All else is local autonomy. Once foreign relations go out of your hands into the charge of somebody else, to that extent and in that measure you are not independent.
(i) In the above passage, the statement was made at which place?
(A) In the Constituent Assembly of India
(B) In the Press Conference at his residence
(C) In the public meeting at Rashtrapati Bhawan
(D) None of the above
(ii) In which year, Jawaharlal Nehru made this statement?
(A) 1947
(B) 1949
(C) 1955
(D) 1958
(iii) What is the fundamental aspect of independence, and how does losing control over it affect a nation’s independence?
Section-E
27. Elaborate about Soviet System. Mention any of the four features of the Soviet System.
OR
If the Soviet Union had not disintegrated and the world had remained bipolar, how would that situation have affected the world politics?
28. Describe any two developments witnessed by India after 1990.
OR
Analyse the formation and objectives of NITI Aayog in present context.
29. Reforming the UN means restructuring of the Security Council. Suggest measures to reform UNSC.
OR
Explain the establishment and objective of UNESCO, UNICEF and ILO in detail.
30. What are the three democratic upsurges that emerged in the post independence history of India? Explain.
OR
Analyse the circumstances that you think were responsible for the declaration of emergency in 1975.
Read Also:
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 1
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 2
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 3
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 4
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 5
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 6
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 7
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 8