If you are a CBSE Class 12 student and Political Science is one of your subjects, then CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1) is extremely important for you. Through this post, we are providing you with free CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Papers to help you prepare effectively for your board exams.
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
These high-quality sample papers are designed to give you a clear understanding of the exam pattern and improve your performance. We hope that practicing these papers will enhance your preparation and enable you to score excellent marks in your board exams. Make the most of this opportunity and give your preparation the edge it needs!
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -9)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Political Science (028)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
3. Section A questions number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries. 1 mark.
4. Section B questions number 13 to 18 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
2 marks. Write answer to each question in 50 to 60 words.
5. Section C questions number 19 to 23 are Long Answer Type-I question. Each question carries
4 marks. Write answer to each question in 100 to 120 words.
6. Section D questions number 24 to 26 are Passage, Cartoon and Map-based questions.
Answer each question accordingly.
7. Section E questions number 27 to 30 are Long Answer Type-II questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
Write answer to each question in 170 to 180 words.
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, note that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
Section-A
1. Nepal transitioned from a monarchy to a federal democratic republic in recent history. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about Monarchy and Democracy in Nepal?
(A) Nepal abolished its monarchy and declared itself a federal democratic republic in 2008.
(B) The transition to democracy in Nepal was marked by a decade-long civil conflict.
(C) The Nepalese monarchy played a central role in the country’s democratic transition without any conflict.
(D) The new constitution of Nepal emphasizes federalism and secularism.
2. Assertion (A): The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a key agency within the United Nations system.
Reason (R): The IMF primarily focuses on providing humanitarian aid to developing countries.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
3. Match the terms given in column ‘A’ correctly with their meaning given in column ‘B’ and choose the appropriate code as the correct answer:
Column A
1. External Security
2. Internal Security
3. Human Security
4. Cybersecurity
Column B
(i) Protection against threats originating outside the nation’s borders.
(ii) Protection against threats within the nation, such as terrorism and insurgency.
(iii) Ensuring the safety of individuals from various threats affecting their well-being.
(iv) Protecting information systems and data from digital attacks and breaches.
Codes:
(A) 1-(i), 2-(ii), 3-(iii), 4-(iv)
(B) 1-(ii), 2-(i), 3-(iv), 4-(iii)
(C) 1-(iii), 2-(iv), 3-(i), 4-(ii)
(D) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(ii), 4-(i)
4. Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The principle of Common but Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) acknowledges that all countries have the same level of responsibility in addressing environmental issues.
Statement II: CBDR allows developed countries to take the lead in addressing environmental issues due to their historical contributions.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(C) Statement I is true, but Statement II is false
(D) Statement I is false, but Statement II is true
5. Arrange the following in chronological order based on their association with globalisation:
I. Formation of the World Trade Organization (WTO)
II. Launch of the Internet
III. Establishment of NAFTA
IV. Creation of the International Criminal Court (ICC)
Choose the correct option:
(A) II, I, III, IV
(B) I, II, III, IV
(C) I, III, II, IV
(D) II, I, IV, III
6. Identify and write the Incorrect pair:
(A) Shock Therapy – Rapid economic liberalization in post-Soviet states
(B) Glasnost – Policy of political openness introduced by Gorbachev
(C) New Economic Policy – Introduced by Lenin in 1921
(D) Brezhnev Doctrine – Policy to maintain the Soviet sphere of influence in Eastern Europe
7. The first general elections in India were a landmark event because they marked the implementation of ____________.
(A) Democratic socialism
(B) Direct presidential election
(C) Universal adult franchise
(D) Party-based voting
8. The First Five Year Plan primarily focused on ____________.
(A) Rapid industrialization and urban development
(B) Developing the agricultural sector and building large dams
(C) Privatization of industries to encourage entrepreneurship
(D) Expanding the IT sector and infrastructure in urban areas
9. Which 1955 conference marked the height of India’s engagement with newly independent Asian and African nations?
(A) Delhi Conference
(B) Bandung Conference
(C) New York Summit
(D) Belgrade Conference
10. Which political alliance was formed by major non-Congress parties in the 1971 election, opposing Indira Gandhi’s Congress?
(A) Grand Alliance
(B) United Democratic Front
(C) Nationalist Coalition
(D) People’s Alliance
11. The slogan “Indira is India, India is Indira” was coined by ____________.
(A) Jayaprakash Narayan
(B) Raj Narain
(C) D.K. Barooah
(D) Morarji Desai
12. Sikkim became a full-fledged state of India in ____________ after a referendum supported by its people.
(A) 1947
(B) 1963
(C) 1975
(D) 1987
Section-B
13. Which are the two forms of co-operative security as per its traditional notion?
14. What is meant by unipolarity and bipolarity?
15. What is meant by ‘coalition’? During which period did this type of government gain popularity for the first time at the centre in India?
16. The first general election was a difficult task for Election Commission. Give two reasons for the same.
17. In recent years India has paid adequate attention to ASEAN. Give two points to justify the statement.
18. South Asia stands for diversity in every sense and yet constitutes one geo-political space. Do you agree with the statement? Give two reasons for your answer.
Section-C
19. What were the reasons for the rise of political violence in the North-Eastern part of India?
20. Mention any two functions of Security Council. Give two reasons why Veto power of the permanent members of Security Council cannot be abolished.
21. The Emergency affected the party system in India, elaborate your answer with examples.
22. “Economic globalisation is recolonization of the world”. Substantiate the statement.
23. What was the major areas of focus of the First Five Year Plan? How was the Second Plan different form the First Plan?
Section-D
24. Study the given cartoon and answer the questions that follow.

(i) What does the cartoon represent?
(A) US’s investment in education and healthcare
(B) US’s massive expenditure on defence and lack of funding for peace-related issues
(C) US’s focus on economic growth
(D) US’s commitment to peace-building efforts
(ii) What message does this cartoon convey?
(A) Countries prioritize peace over military spending
(B) Countries are more willing to invest in military than in peace efforts
(C) Countries are equally balancing military and peace expenditures
(D) Countries neglect military spending entirely
(iii) How is this situation different from India?
(A) India spends only on defense
(B) India spends on both defense and peaceful initiatives, with a focus on peaceful solutions first
(C) India neglects peace-related initiatives entirely
(D) India avoids defense expenditure
(iv) What does the cartoon imply about global priorities?
(A) Equal focus on peace and defense
(B) Neglect of peace efforts in favor of military expenditures
(C) Preference for economic development over defense
(D) Promotion of international peace treaties
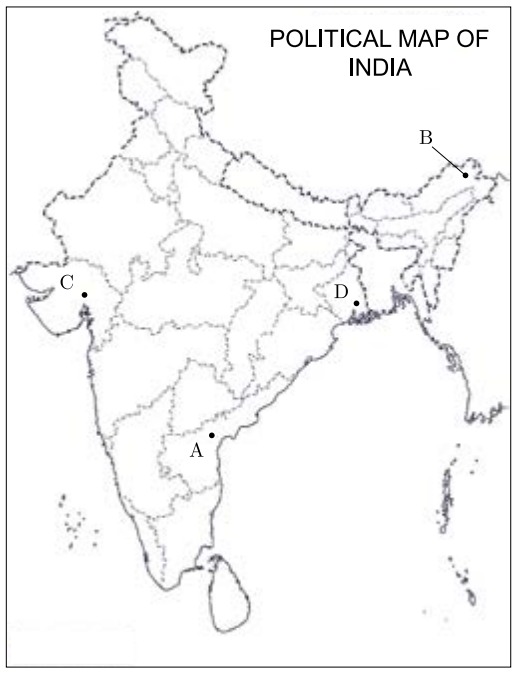
25. In the given map of India four states have been marked as (A), (B), (C) and (D). Identify these states on the basis of the information given below and writer their correct names in respective serial number. Information given about the Lok Sabha election results 1977.
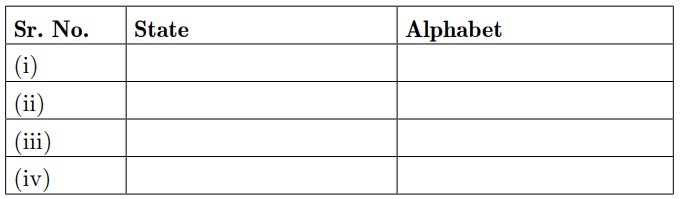
(i) The state where India National Congress (INC) was in majority.
(ii) The state were Janata Party was in majority.
(iii) The state where other parties were in majority.
(iv) The state where left parties were in majority.
26. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
We have a Muslim minority who are so large in number that they cannot, even if they want, go anywhere else. That is a basic fact about which there can be no argument. Whatever the provocation from Pakistan and whatever the indignities and horrors inflicted on non-Muslims there, we have got to deal with this minority in a civilised manner. We must give them security and the rights of citizens in a democratic state. If we fail to do so, we shall have a festering sore which will eventually poison the whole body politic and probably destroy it. Jawaharlal Nehru, letter to Chief Ministers, 15th October, 1947.
(i) The speaker of the given passage was_____.
(A) Mohammad Ali Jinnah
(B) Jawaharlal Nehru
(C) Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan
(D) Mohammad Iqbal
(ii) Why Jawaharlal Nehru wanted to deal with the Muslim minority in a civilised way?
(A) Because Muslim minority were in large number in India.
(B) Because it is their right to go anywhere i.e. to go Pakistan or stay in India.
(C) Because in a democratic set-up everyone should be given an equal opportunity.
(D) All of the above
(iii) What stance does Jawaharlal Nehru advocate for dealing with the Muslim minority in India, as expressed in his letter to the Chief Ministers dated 15th October 1947, and what consequences does he foresee if this approach is not followed?
Section-E
27. What does ASEAN stand for? What are the main objectives of ASEAN?
OR
Differentiate between European Union and SAARC as new centres of power.
28. What were the consequences of the partition of India in 1947.
OR
Why did Jawaharlal Nehru try to keep India, a secular country? Do you think whether the reasons were ethical and sentimental? Give reasons for the same.
29. Explain the second phase of Indian politics towards a multi-party coalition system with reference to general elections of 1967.
OR
Explain the philosophy of Integral Humanism given by Pandic Deendayal Upadhyaya.
Read Also:
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 1
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 2
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 3
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 4
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 5
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 6
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 7
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 8
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 9