If you are a CBSE Class 12 student and Political Science is one of your subjects, then CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1) is extremely important for you. Through this post, we are providing you with free CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Papers to help you prepare effectively for your board exams.
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
These high-quality sample papers are designed to give you a clear understanding of the exam pattern and improve your performance. We hope that practicing these papers will enhance your preparation and enable you to score excellent marks in your board exams. Make the most of this opportunity and give your preparation the edge it needs!
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -4)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Political Science (028)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
3. Section A questions number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries. 1 mark.
4. Section B questions number 13 to 18 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
2 marks. Write answer to each question in 50 to 60 words.
5. Section C questions number 19 to 23 are Long Answer Type-I question. Each question carries
4 marks. Write answer to each question in 100 to 120 words.
6. Section D questions number 24 to 26 are Passage, Cartoon and Map-based questions.
Answer each question accordingly.
7. Section E questions number 27 to 30 are Long Answer Type-II questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
Write answer to each question in 170 to 180 words.
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, note that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
Section-A
1. International Organizations play a crucial role in global governance and cooperation. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about International Organisations?
(A) International Organizations facilitate cooperation between countries on various global issues.
(B) The United Nations is the only international organization that exists.
(C) International Organizations can include both governmental and non-governmental entities.
(D) Organizations like the IMF and World Bank are key players in the global economic landscape.
2. Assertion (A): Traditional security primarily deals with military threats to a nation.
Reason (R): Non-traditional security issues like environmental degradation are included within traditional security frameworks.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
3. Match the terms given in column ‘A’ correctly with their meaning given in column ‘B’ and choose the appropriate code as the correct answer:
Column A
1. Global Commons
2. Common but Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR)
3. Resource Geopolitics
4. Rights of Indigenous Peoples
Column B
(i) Areas like the atmosphere and oceans that are not owned by any single nation.
(ii) A principle acknowledging different capabilities and responsibilities of countries in environmental conservation.
(iii) The strategic importance and competition over natural resources on a global scale.
(iv) Legal and moral rights of native communities to their ancestral lands and cultures.
Codes:
(A) 1-(i), 2-(ii), 3-(iii), 4-(iv)
(B) 1-(ii), 2-(i), 3-(iv), 4-(iii)
(C) 1-(iii), 2-(iv), 3-(i), 4-(ii)
(D) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(ii), 4-(i)
4. Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Globalisation involves the integration of economies, cultures, and political systems across the world.
Statement II: Globalisation has led to the complete isolation of national economies from each other.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(C) Statement I is true, but Statement II is false
(D) Statement I is false, but Statement II is true
5. Arrange the following events in chronological order of their occurrence:
I. Introduction of Perestroika
II. Fall of the Berlin Wall
III. Dissolution of the Soviet Union
IV. Implementation of Shock Therapy in Russia
Choose the correct option:
(A) I, II, III, IV
(B) II, I, IV, III
(C) I, II, IV, III
(D) I, IV, II, III
6. Identify and write the Incorrect pair:
(A) European Union – Consists of 27 European countries
(B) ASEAN – Association of South Asian Nations
(C) NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization
(D) BRICS – Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
7. What was the primary goal of India’s foreign policy in the early years after independence?
(A) To become a member of the Western bloc
(B) To gain economic aid from colonial powers
(C) To maintain territorial integrity, sovereignty, and promote economic development
(D) To join military alliances to counter regional threats
8. After the sudden death of Lal Bahadur Shastri, which two leaders contended for the position of Prime Minister?
(A) K. Kamraj and Morarji Desai
(B) Morarji Desai and Indira Gandhi
(C) Indira Gandhi and Atulya Ghosh
(D) S.K. Patil and K. Kamraj
9. What was the primary slogan of Indira Gandhi during the 1971 elections, which was questioned due to the economic crisis in the early 1970s?
(A) Jai Hind
(B) Vande Mataram
(C) Garibi Hatao
(D) Bharat Mata Ki Jai
10. The Assam Movement (1979-1985) was largely fuelled by concerns over ____________.
(A) Economic development in rural areas
(B) Large-scale immigration from Bangladesh
(C) Agricultural land reforms
(D) Partition of Assam from Meghalaya
11. Which Prime Minister’s assassination in 1991 led to the appointment of P.V. Narasimha Rao as Congress leader?
(A) Indira Gandhi
(B) Rajiv Gandhi
(C) Lal Bahadur Shastri
(D) Morarji Desai
12. Which language group became the first to successfully advocate for state reorganization based on linguistic lines in post-independence India?
(A) The Bengali-speaking population seeking recognition of their language
(B) The Punjabi-speaking communities who sought a state reflecting their identity
(C) The Telugu-speaking population in Andhra Pradesh advocating for linguistic statehood
(D) The Tamil-speaking people of the southern region, striving for state reorganization
Section-B
13. What was the reason behind newspapers being censored during Emergency?
14. What are the two issues that dominate the politics of North-East India.
15. What do you understand by decentralised planning?
16. What is ‘Two-Nation theory’?
17. Explain any of the two principles of Nehru’s Foreign Policy.
18. What is non-Congressism?
Section-C
19. What is International Labour Organisation? Mention its objectives.
20. What are two positive and two negative effects of globalisation? Explain.
21. Describe any four consequences of Bangladesh War of 1971.
22. Briefly discuss the relations between India and Israel.
23. Who was Jayaprakash Narayan and what did he advocate?
Section-D
24. Observe the picture given below and answer the following questions.

(i) In which year did the bipolar structure of world politics end?
(A) 1989
(B) 1990
(C) 1991
(D) 1992
(ii) Which two associations of nations emerged in Europe and Asia?
(A) NATO and SAARC
(B) European Union and ASEAN
(C) Warsaw Pact and SEATO
(D) None of the above
(iii) In which year did the revolution in China take place, marking the beginning of Communist China?
(A) 1945
(B) 1947
(C) 1949
(D) 1950
(iv) What does the slogan “The Socialist Road is the Broadest of All” signify?
(A) The adoption of a capitalist economy
(B) The guiding ideology of China’s early phase after the revolution
(C) The rejection of socialism in favour of communism
(D) The prioritization of foreign trade
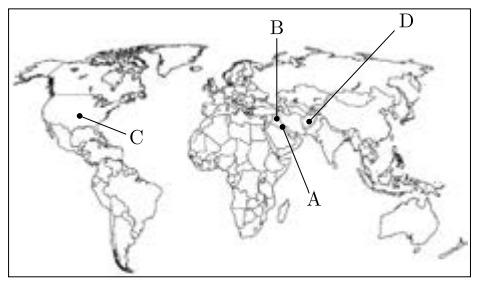
25. In the given outline map of world, four countries have been marked as A, B, C and D. Identify these on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with the respective serial numbers of the information used and the concerned alphabets as per the format that follows.
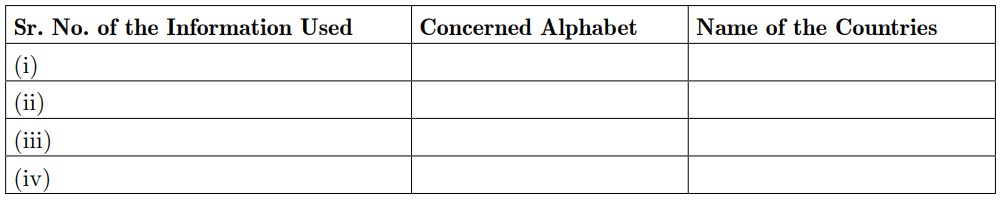
(i) The country Iraq invaded in August 1990.
(ii) The country in the Presidentship of Saddam Hussein.
(iii) The country referred to as a Hegemonic Power.
(iv) The Operation Infinite Reach was launched against this country.
26. Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions that follow. America extended massive financial help for reviving Europe’s economy under what was called the ‘Marshall Plan’. The US also created a new Collective Security structure under NATO. Under the Marshall Plan, the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was established in 1948 to channel aid to the West European States. It became a forum where the Western European States began to cooperate on trade and economic issues. The Council of Europe, established in 1949, was another step forward in political cooperation. The process of economic integration of European capitalist countries proceeded step by step leading to the formation of the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957.
(i) The financial help was extended by America for reviving ______ economy.
(A) African
(B) European
(C) Asian
(D) American
(ii) What was the collective security structure created by the US?
(A) NATO
(B) SEATO
(C) CENTO
(D) Any other
(iii) How did the Marshall Plan contribute to the economic and political integration of Western Europe?
Section-E
27. What were the two Secessionist Movements of the North-East India?
OR
Explain three main causes behind the unrest in the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
28. Explain the role of opposition parties in India.
OR
What were the reasons behind the dominance of Congress party in the first three general elections of India?
29. “Coalition government is good or bad for the Indian democracy”. Explain three points in support of your answer.
OR
Analyse the era of Multi-Party system in India after 1989.
30. What role India played in the Afro-Asian Unity? Explain.
OR
Analyse the India-Russia relations in detail.
Read Also:
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 1
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 2
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 3
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 4
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 5
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 6
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 7
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 8