If you are a CBSE Class 12 student and Political Science is one of your subjects, then CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -1) is extremely important for you. Through this post, we are providing you with free CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Papers to help you prepare effectively for your board exams.
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
These high-quality sample papers are designed to give you a clear understanding of the exam pattern and improve your performance. We hope that practicing these papers will enhance your preparation and enable you to score excellent marks in your board exams. Make the most of this opportunity and give your preparation the edge it needs!
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper (Set -5)
Class – 12th Exam – 2024 – 25
Political Science (028)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
3. Section A questions number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries. 1 mark.
4. Section B questions number 13 to 18 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
2 marks. Write answer to each question in 50 to 60 words.
5. Section C questions number 19 to 23 are Long Answer Type-I question. Each question carries
4 marks. Write answer to each question in 100 to 120 words.
6. Section D questions number 24 to 26 are Passage, Cartoon and Map-based questions.
Answer each question accordingly.
7. Section E questions number 27 to 30 are Long Answer Type-II questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
Write answer to each question in 170 to 180 words.
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, note that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
Section-A
1. Security in the contemporary world encompasses both traditional and non-traditional aspects.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about the Meaning and Type of Security?
(A) Traditional security focuses solely on military threats to a nation.
(B) Non-traditional security includes issues like human rights and environmental threats.
(C) Security now includes both external and internal dimensions.
(D) Traditional security has expanded to incorporate economic and social factors.
2. Assertion (A): Global commons include areas like the atmosphere and oceans, which are not owned by any single country.
Reason (R): The management of global commons requires international cooperation among nations.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
3. Match the terms given in column ‘A’ correctly with their meaning given in column ‘B’ and choose the appropriate code as the correct answer:
Column A
1. Globalisation
2. Economic Liberalization
3. Resistance to Globalisation
4. Cultural Homogenization
Column B
(i) The process of reducing trade barriers and opening up economies to foreign investment.
(ii) The increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of global economies, cultures, and political systems.
(iii) Opposition to the process of global integration due to various social, economic, and cultural concerns.
(iv) The blending of diverse cultures into a single, uniform culture. Codes:
(A) 1-(ii), 2-(i), 3-(iii), 4-(iv)
(B) 1-(i), 2-(ii), 3-(iv), 4-(iii)
(C) 1-(iii), 2-(iv), 3-(i), 4-(ii)
(D) 1-(iv), 2-(iii), 3-(ii), 4-(i)
4. Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The Soviet Union was established in 1922 after the Russian Revolution.
Statement II: The Soviet system was characterized by a multi-party political structure.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(B) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(C) Statement I is true, but Statement II is false
(D) Statement I is false, but Statement II is true
5. Arrange the following organizations and initiatives in chronological order of their establishment:
I. Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
II. European Union (EU)
III. Belt and Road Initiative
IV. Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
Choose the correct option:
(A) I, II, IV, III
(B) II, I, III, IV
(C) I, II, III, IV
(D) I, II, IV, III
6. Identify and write the Incorrect pair:
(A) Pakistan – Experienced multiple military coups
(B) Bangladesh – Struggled with establishing stable democracy
(C) Nepal – Remained a monarchy till present
(D) Sri Lanka – Faced ethnic conflicts impacting democracy
7. The slogan “Jai Jawan Jai Kisan” symbolized India’s focus on ____________.
(A) Youth empowerment and education
(B) Military strength and agricultural productivity
(C) Industrialization and foreign policy
(D) Women’s rights and urban development
8. The “Total Revolution” movement, which played a role in opposing the Emergency, was led by ____________.
(A) George Fernandes
(B) Morarji Desai
(C) Jayaprakash Narayan
(D) D.K. Barooah
9. Operation Blue Star, conducted in 1984, aimed to ____________.
(A) Prevent foreign invasions
(B) Provide economic relief to farmers
(C) Remove militants from the Golden Temple in Amritsar
(D) Merge Punjab with Haryana
10. The BJP adopted which ideological concept as part of its political platform after 1986?
(A) Secularism
(B) Hindutva
(C) Gandhian Socialism
(D) Marxism
11. Who among the following leaders played a pivotal role in integrating the princely states into the Union of India following independence?
(A) Mahatma Gandhi, known for his philosophy of non-violence and satyagraha
(B) Jawaharlal Nehru, who served as India’s first Prime Minister and emphasized unity
(C) B.R. Ambedkar, the principal architect of the Indian Constitution
(D) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, the Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister of India
12. The Socialist Party separated from the Congress in 1948 due to _________.
(A) Political rivalry with Nehru
(B) Disagreements on caste policies
(C) A policy change preventing dual membership
(D) Regional language issues
Section-B
13. Mention any two measures to have good relations with Pakistan.
14. What prompted nationwide Satyagraha against Congress?
15. Identify any two outcomes of the Partition of India into India and Pakistan.
16. Differentiate between ‘one-party dominance’ and ‘one party system’.
17. What are the two models of development and which of the models were adopted by India?
18. What was the purpose of Operation Desert Storm’?
Section-C
19. Analyse the consequences of the Chinese invasion of 1962 in hampering India’s image at home and abroad.
20. What is UNICEF? Mention any four functions performed by it?
21. What are the major problems of ecological issues?
22. What is the difference between refugees and migrants?
23. Enlist any four features of the Congress Party.
Section-D
24. Study the picture given below carefully and answer the following questions.

(i) What does the picture depict?
(A) War and destruction
(B) Peace being at stake
(C) Growth and development
(D) Celebration of peace
(ii) How is regionalism defined?
(A) A theory emphasizing global unity
(B) A theory emphasizing regional characteristics and local issues
(C) A practice of ignoring local issues for national interests
(D) A focus on international trade
(iii) What does the arrow hitting the pigeon symbolize?
(A) An attack on communication systems
(B) A threat to peace
(C) Destruction of nature
(D) A warning to nations
(iv) What is the white pigeon a symbol of in the picture?
(A) War
(B) Freedom
(C) Peace
(D) Prosperity
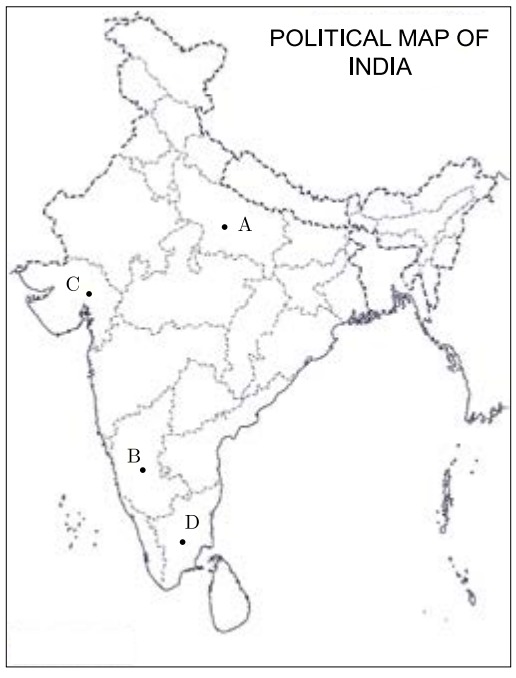
25. In the give outline political map of India four states have been marked as A, B, C and D.
Identify these states on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book with their respective serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabets as per format that follows.
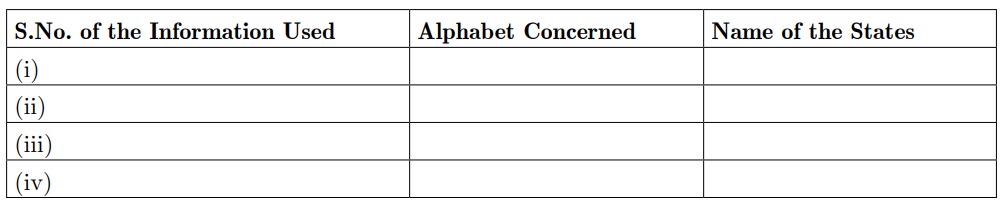
(i) The state to which Minister for Communications in the first ministry of free India belonged.
(ii) The state to which the former Prime Minister Morarji Desai was related.
(iii) The state to which S. Nijalingappa belonged.
(iv) The state related to former Congress President K. Kamraj.
26. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
Globalisation does not always reduce state capacity. The primacy of the state continues to be unchallenged basis of political community. The old jealousies and rivalries between countries have not ceased to matter in world politics. The state continues to discharge its essential functions (law and order, national security) and consciously withdraws from certain domains from which it wishes to. States continue to be important. Indeed, in some respects state capacity has received a boost as a consequence of globalisation, with enhanced technologies available at the disposal of the state to collect information about its citizens.
(i) Globalisation has given boost to the state capacity because______.
(A) state has become more market centric in approach which is beneficial for the people
(B) state has increased its welfare capacity through globalisation
(C) it has made available advance technology to state to rule its people better
(D) None of the above
(ii) The primacy of the state continues to be unchallenged basis of______.
(A) international interests
(B) security threats
(C) welfarism
(D) political community
(iii) How do enhanced technologies enable the state to rule better?
Section-E
27. “Peace and Prosperity of countries lay in the establishment and strengthening of regional
economic organisations”. Critically analyse the statement.
OR
What is Godhra riots? What were its outcomes?
28. How Bangladesh was formed as an independent nation?
OR
What are the efforts which has been taken by India and Pakistan towards peace and cooperation
between both the nation?
29. Analyse the philosophy of Integral Humanism advocated by Pandit Deendayal Upadhayaya.
OR
What was the major outcome of 1977 Lok Sabha elections? Explain.
30. Define the term Unipolarity. What were the outcomes of a unipolar world after 1991 that
benefitted USA?
OR
What was the Gulf War of 1990?
Read Also:
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 1
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 2
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 3
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 4
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 5
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 6
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 7
CBSE Board Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper SET – 8